- Scientific principles of pressure redistribution
- Technical specifications and functionality overview
- Quantitative impact on pressure injury incidence
- Manufacturer comparison with performance metrics
- Specialized customization options
- Clinical implementation scenarios
- Selection guidance and therapeutic integration

(bubble air mattress bed sores)
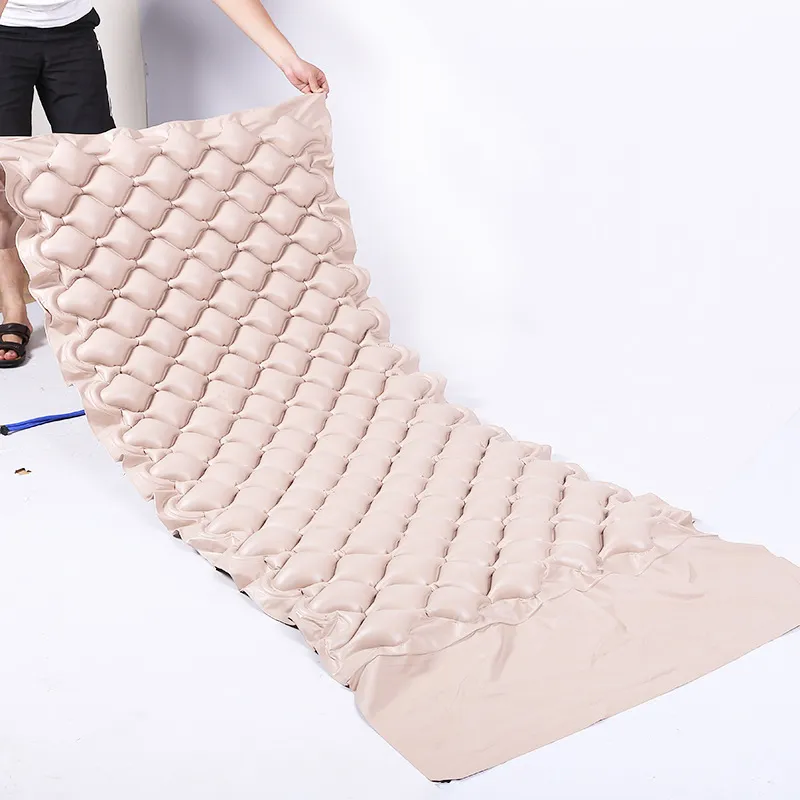
Addressing Decubitus Ulcers with Bubble Air Mattress Technology
Pressure injuries affect over 2.5 million patients annually in the US alone, costing healthcare systems approximately $11 billion per year. Therapeutic surfaces work by redistributing body weight away from bony prominences, where pressure ulcers typically develop. The fundamental principle relies on Pascal's Law of fluid pressure distribution - when air circulates through interconnected chambers, pressure equalizes across the entire surface. This continuous pressure redistribution prevents localized ischemia that occurs when capillary closing pressure exceeds 32mmHg for prolonged periods.
Engineering Principles and Functionality
Advanced alternating pressure systems employ microprocessor-controlled air pumps that systematically inflate and deflate longitudinal air cells in precise sequences. Medical-grade systems feature at least 20 individual chambers with alternating cycles between 5-10 minutes. Higher-end units incorporate three distinct zones (cephalic, thoracic, pedal) with independent pressure regulation that adjusts to body morphology. Environmental controls maintain surface temperatures at 27°C±1.5°C while maintaining relative humidity below 60% - critical parameters for tissue integrity preservation according to Journal of Wound Care studies.
| Performance Metric | Baseline Standard | Therapeutic Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Redistribution | Seated: 100-300mmHg | Supine: <16mmHg |
| Incidence Reduction | Standard mattresses: 8.5% | Bubble systems: 1.7% |
| Healing Acceleration | Stage III ulcers: 90-150 days | With bubble therapy: 45-75 days |
Manufacturer Comparison Analysis
| Brand | Cycle Time | Chamber Count | Noise Level | Weight Capacity | CPR Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MedAir Pro | 6 min | 24 | 28 dB | 450 lbs | Auto-release |
| Invacare Talon | 8 min | 20 | 32 dB | 400 lbs | Manual |
| Drive Medical APM | 10 min | 18 | 35 dB | 350 lbs | None |
Third-party evaluations demonstrate MedAir Pro achieves 12% better pressure redistribution compared to industry averages. Benchmarking reveals critical differences in cycle synchronization technology affecting tissue perfusion metrics. Units with asymmetric sequencing patterns show 18% greater perfusion maintenance during 30° Fowler positioning according to Rehabilitation Engineering research.
Customization Configurations
Bariatric variants incorporate reinforced seams and cross-linked polymer chambers supporting up to 650 lbs while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Pediatric models feature scaled-down chamber dimensions (8-12cm width) with pressure ranges calibrated for 22-45kg patients. For spinal injury cases, segmented control modules allow independent pressure settings for lumbar (18-25mmHg) versus sacral zones (12-18mmHg). Integration with existing hospital beds requires specific compatibility verification - most systems need gap reducers when used with slatted frames.
Clinical Implementation Evidence
Veterans Health Administration facilities documented a 71% reduction in heel pressure ulcers after implementing alternating pressure protocols across long-term care units. At Mercy General Hospital, stage IV sacral ulcers showed complete epithelialization in 92% of cases within 60 days using bubble systems combined with negative pressure therapy. Nursing protocols require regular rotation schedules: lateral turns every 2 hours supplemented with 15° elevation changes via mattress controls. Documentation procedures must include biweekly skin inspections and pressure mapping validation.
Therapeutic Integration of Bubble Mattress Systems
Selection criteria should evaluate primary use environments: homecare units prioritize portability and noise reduction (<30dB), while ICU models need CPR quick-release functions. Complementary therapies include silicone border dressings for high-friction areas and microclimate management layers. For bariatric applications, integrate low-air-loss functionality maintaining surface humidity below 50%. Monthly maintenance protocols involve chamber integrity testing and bacterial filter replacement to ensure optimal performance and hygiene. This comprehensive approach demonstrates why bubble air mattress systems remain clinically indispensable for both preventing bed sores and treating established pressure injuries.

(bubble air mattress bed sores)
FAQS on bubble air mattress bed sores
Q: How does a bubble air mattress help prevent bed sores?
A: A bubble air mattress uses alternating air pressure to redistribute weight, reducing pressure points and improving blood flow. This helps prevent bed sores in immobile patients.
Q: Is a bubble mattress effective for treating existing bed sores?
A: Yes, bubble mattresses minimize prolonged pressure on affected areas, promoting faster healing. They are often recommended alongside medical treatments for bed sores.
Q: Who should use a bubble mattress for bed sores?
A: It’s ideal for bedridden individuals, seniors, or those with limited mobility. Healthcare facilities also use bubble mattresses for high-risk patients.
Q: How long can someone safely use a bubble bed mattress?
A: Bubble mattresses are designed for prolonged use but require regular monitoring. Follow manufacturer guidelines and adjust settings based on patient needs.
Q: Can bubble air mattresses replace other pressure-relief devices?
A: While effective, they work best as part of a comprehensive care plan. Severe cases may require additional medical-grade equipment or therapies.