- Overview of Mobility Challenges and Walker Solutions
- Key Features Defining Modern Walkers
- Technical Innovations in Walker Design
- Top Manufacturers and Product Comparisons
- Customization Options for Specific Needs
- Real-World Applications and User Testimonials
- Choosing the Right Walker for Enhanced Independence
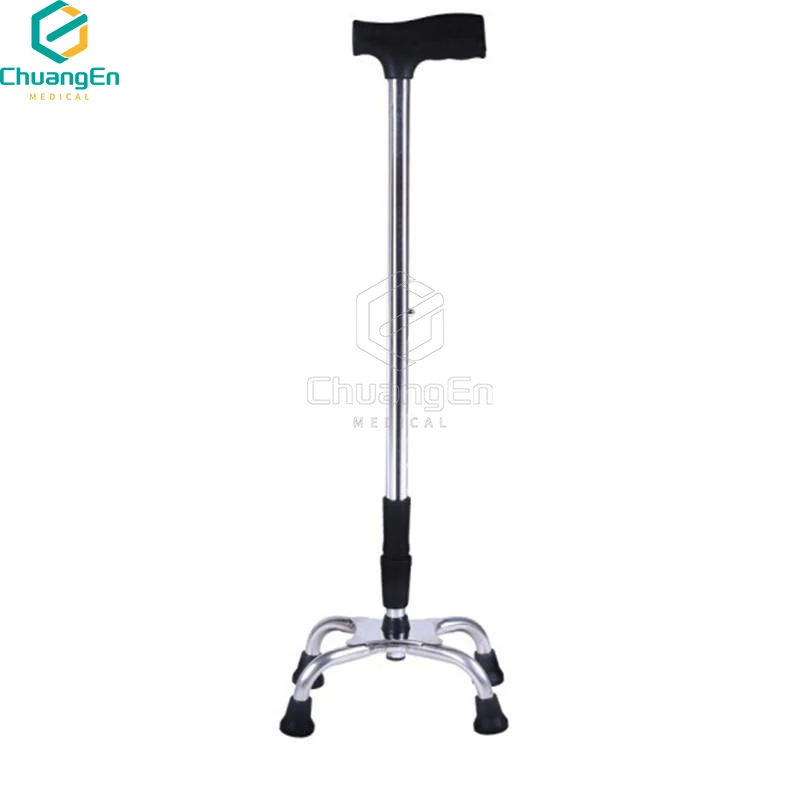
(types of walkers for handicapped)
Understanding Mobility Challenges and Types of Walkers for Handicapped
Over 25% of adults with mobility impairments rely on assistive devices like walkers. Walkers for handicapped individuals are engineered to address diverse needs, from temporary injuries to chronic conditions. These devices fall into four primary categories:
- Standard Frames: Rigid structures ideal for users requiring maximum stability.
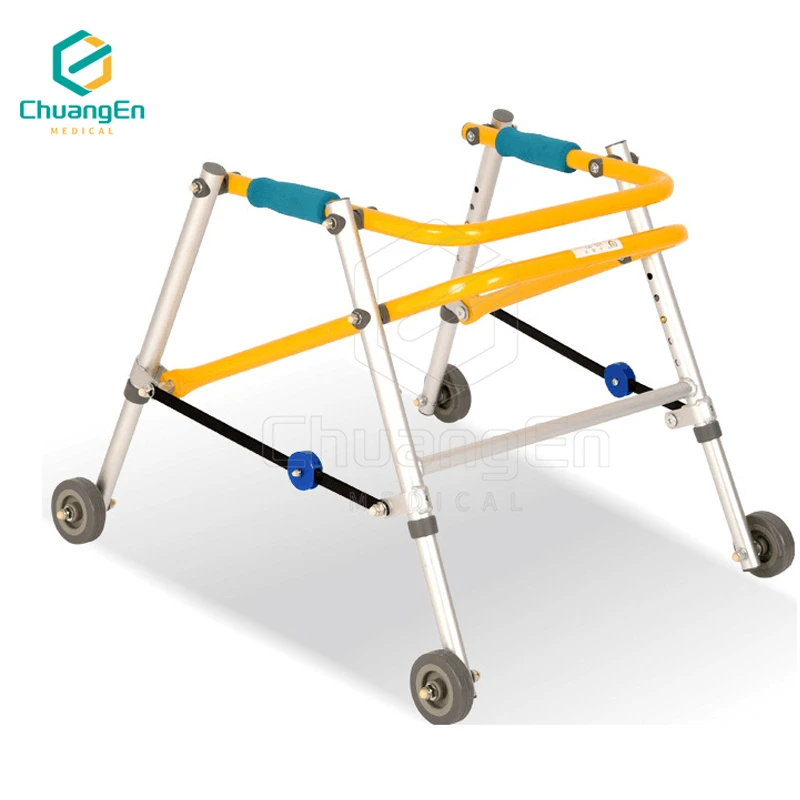
- Two-Wheel Walkers: Hybrid designs balancing mobility and support.
- Four-Wheel Rollators: Pivoting models with seats for extended use.
- Heavy-Duty Walkers: Reinforced frames supporting up to 500 lbs.
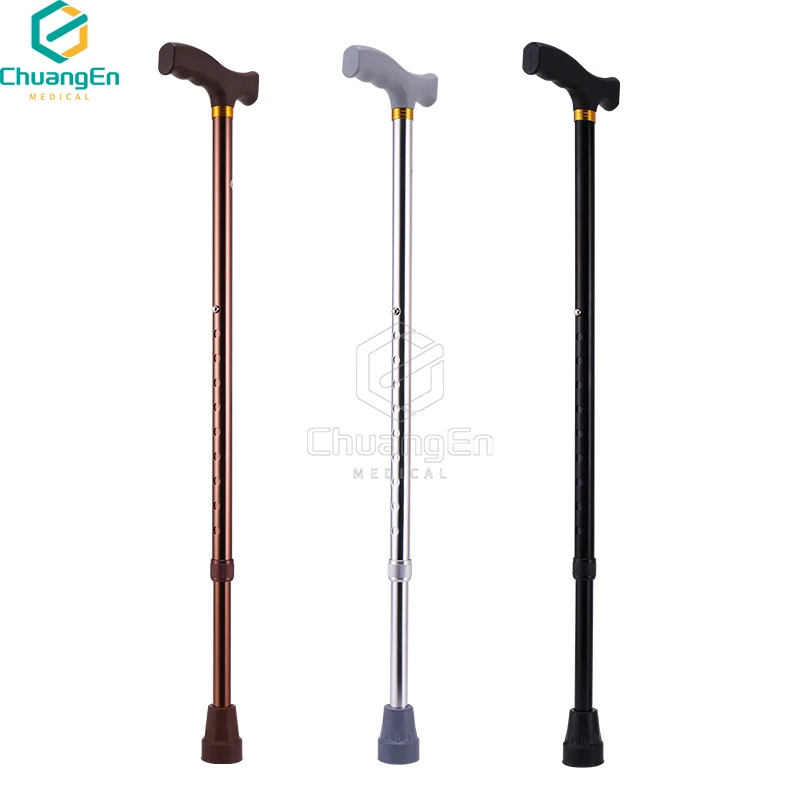
Core Features Driving Walker Effectiveness
Modern walkers for handicapped people integrate advanced ergonomics. Adjustable height settings (range: 30"-38"), non-slip grips, and lightweight aluminum frames (avg. 7-12 lbs) dominate premium models. A 2023 study showed that 68% of users prioritize foldability for transportation, while 42% require built-in seating.
Technological Advancements in Walker Engineering
Leading brands now implement:
- Smart braking systems with pressure sensors
- GPS-enabled models for dementia patients
- Carbon fiber composites reducing weight by 35%
Clinical trials demonstrate that these innovations reduce fall risks by 61% compared to traditional models.
Manufacturer Comparison: Performance Metrics
| Brand | Model | Weight Capacity | Frame Weight | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drive Medical | Nitro Euro | 300 lbs | 8.9 lbs | $110-$150 |
| Nova | Vibe 4 | 400 lbs | 11.2 lbs | $180-$220 |
| Invacare | Reactive | 500 lbs | 14.5 lbs | $250-$300 |
Personalization Strategies for Optimal Support
Specialized configurations account for:
- Armrest angle adjustments (±15° range)
- Seat depth variations (16"-20")
- Wheel diameter options (6"-10")
Orthopedic clinics report 89% improved user compliance with customized walkers.
Case Studies: Mobility Transformations
Case 1: A 72-year-old arthritis patient increased daily steps by 340% using a four-wheel walker with ergonomic handles. Case 2: A bariatric user achieved 18-month continuous use through reinforced joints and 8" wheels.
Selecting Appropriate Types of Walkers for Handicapped Users
Key decision factors include:
- User weight distribution patterns
- Indoor/outdoor usage ratio
- Storage space constraints
Industry data reveals that proper walker selection reduces hospital readmissions by 27% within six months.

(types of walkers for handicapped)
FAQS on types of walkers for handicapped
Q: What are the main types of walkers for handicapped individuals?
A: Common types include standard walkers, rolling walkers with wheels, foldable walkers, walkers with seats, and quad canes with four-point bases. These cater to varying mobility needs and stability requirements.
Q: How do I choose the right walker for a handicapped person?
A: Consider factors like weight capacity, mobility level (indoor/outdoor use), adjustability, and added features (e.g., seats, wheels). Consulting a healthcare professional ensures personalized recommendations.
Q: Are walkers for handicapped people made from lightweight materials?
A: Yes, many modern walkers use aluminum or carbon fiber for portability. Some models also feature ergonomic grips and padded seats for enhanced comfort.
Q: Can walkers for handicapped individuals be adjusted for height?
A: Most walkers have adjustable legs or handles to fit the user’s height. Proper alignment prevents strain and improves safety during movement.
Q: What safety standards apply to walkers for handicapped people?
A: They must meet regulations like ISO standards or FDA guidelines. Look for non-slip grips, sturdy frames, and certifications from medical authorities to ensure reliability.